562
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
this post was submitted on 11 Dec 2023
562 points (98.4% liked)
Linux
48775 readers
618 users here now
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
founded 5 years ago
MODERATORS

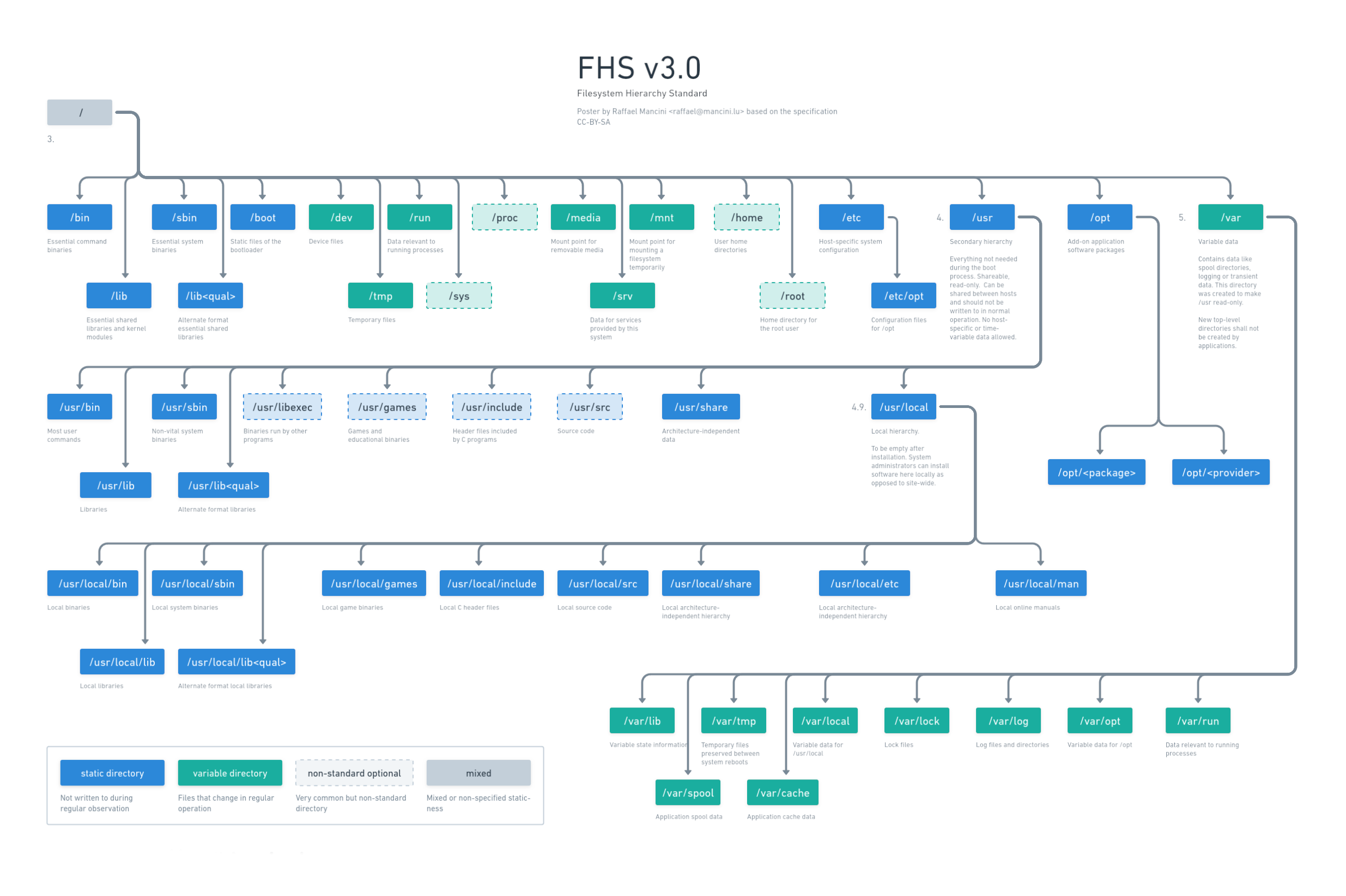
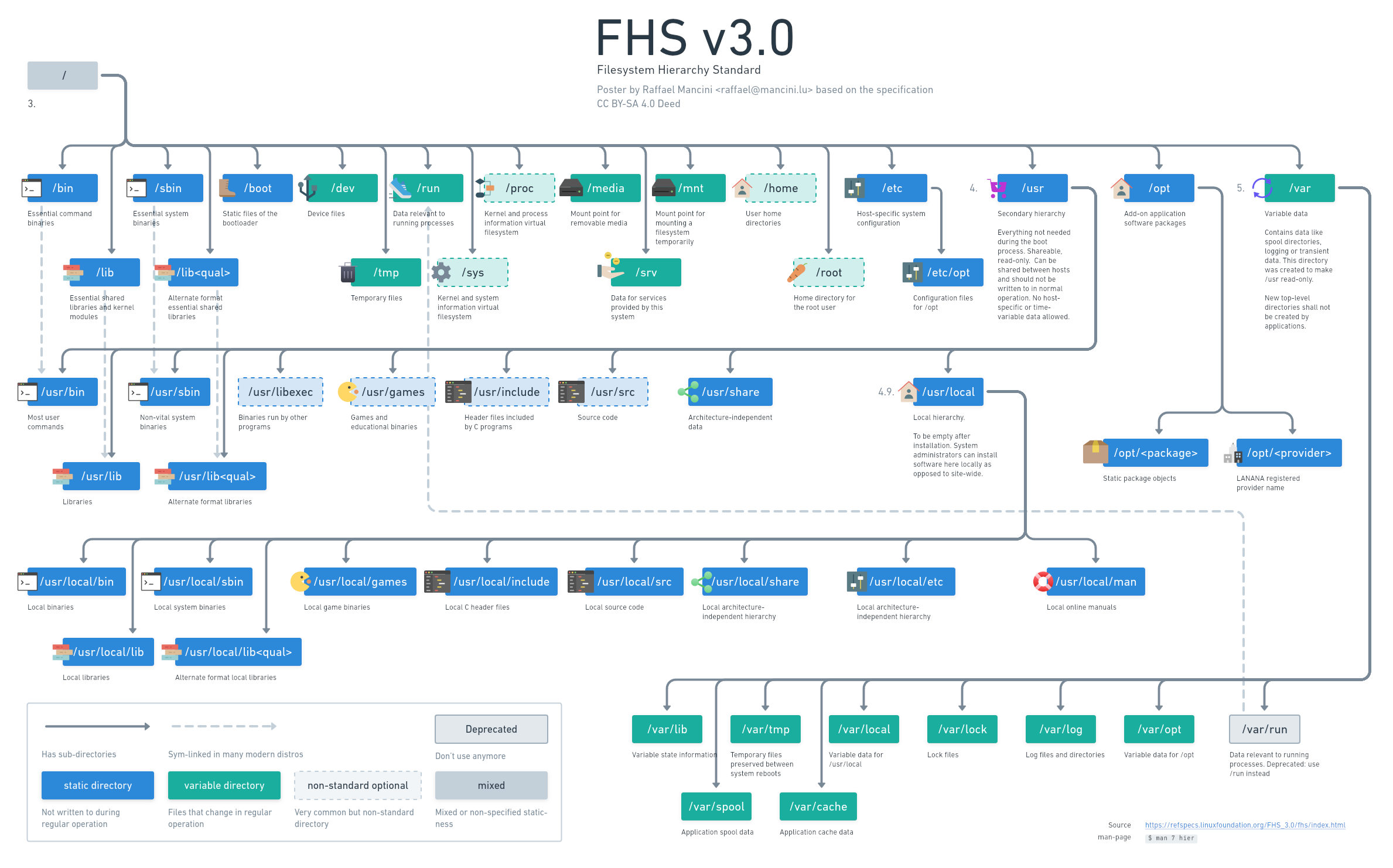
I don't understand the ambiguity of where to put your projects.
I've typically always put things under /opt/ TIL /etc/opt was where the config should go.
Depends on the scope of your project. But if they are services for example or you want them to be run by different users on the system, you could either use /opt or /usr/local. There is some discussion about which is better or how to choose: eg. https://www.linuxjournal.com/magazine/pointcounterpoint-opt-vs-usrlocal . The FHS is mostly relevant when packaging your software though.
Less relevant with Docker or FlatPaks though right?
I'm not into those since they just shift the complexity. People should learn how to package things and just do it. Ok, documentation on making dpkgs is pretty tough to understand and confusing.
But yeah, I guess with docker it's complete anarchy ( the bad kind of)
Not really, usually stuff will be all self contained (no pun intended), container volumes inside docker's own directory and mounts of folders that will most often all reside under the same repository, then you don't have to worry about breaking stuff by touching the root, even better if you do that with Podman.
Flatpak is similar in the way that it also has its own standards and apps are pretty much obligated to follow them. Now the fact that data lives under
.var/app/completely disregarding the XDG spec, while both things are part of Freedesktop... Well that's just ironic lolBut who knows what's inside?
Not at all true. Go inspect the Dockerfile. If done correctly you should be able to inspect the full container build.
Of course you can, but few people care and do it. There is a saying about docker: "Docker images are like smoothies, you immediately know if you like it but you don't know what's inside". The idea being that there is no good quality control and transparency. People just install random blobs, like in the old days where you would install a cracked game from eMule.
If you care about security, docker is not what you want, they are not reproducible nor transparent nor is it possible to easily update broken shared libraries (eg openssl).
But then again people have different requirements. Some just wanna have things running quickly without the hassle. That's where docker shines. But it leads us to a world where we hide ugly stuff under the carpet instead of fixing things.
Agreed but can't the same be said about pre-compiled binaries?
At least with a Dockerfile I can download the repo and make them image for myself.
Sure you could've downloaded the repo and compiled the binary for yourself but you still had to have all of the libraries setup correctly. It's more about a codified build process that's reproducible vs a "supposedly" working documentation on a git repo of make scripts.
There is a lot of work being done on reproducible builds in the guix project and other distros. The idea being that you can be sure that a binary package is bit for bit the same, whoever builds it and on whatever system. This would be the first time you have complete traceability of what goes into your binaries.
On guix, you can for example install substitutes of packages which you could also build manually. Since the build environment and the dependencies are very tightly controlled, you have mathematical proof that the substitute is equivalent to the package built by the maintainer. You can thus be sure that no evil third party injected malware into the substitute binary, unless ot was done at source code level and the package maintainer has put it there (by accident).